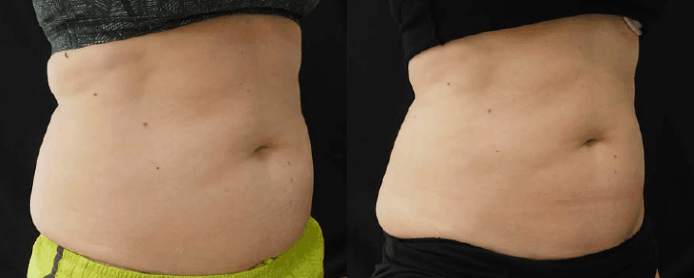
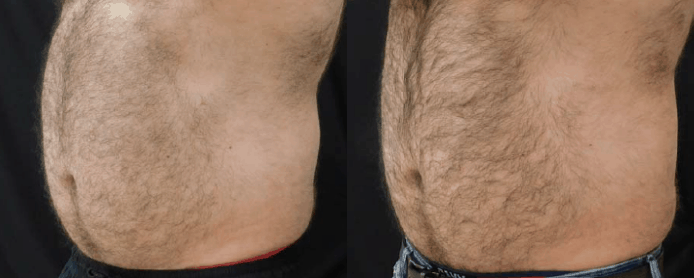
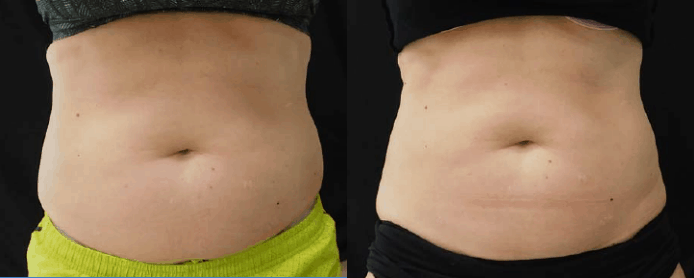
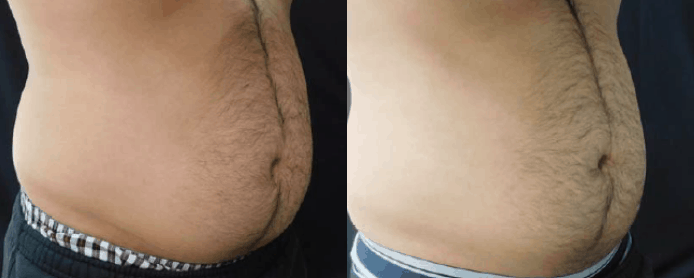
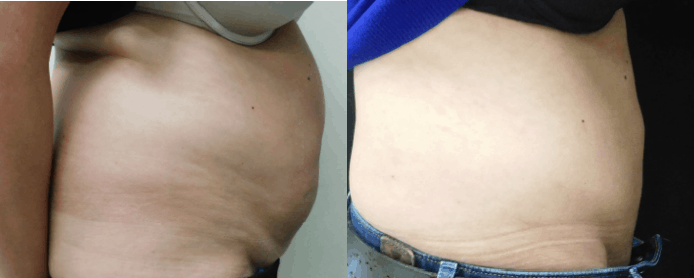
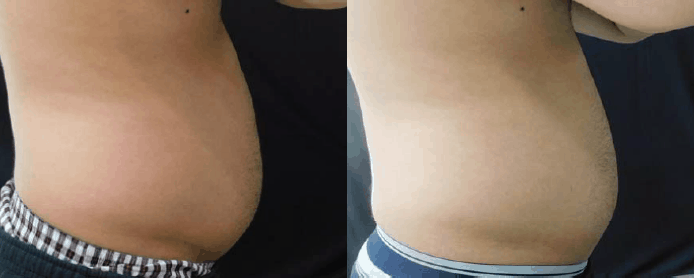
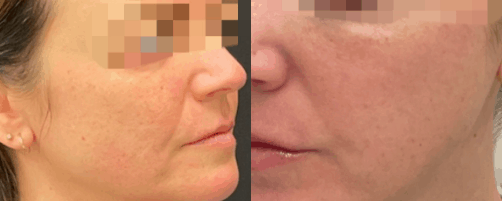
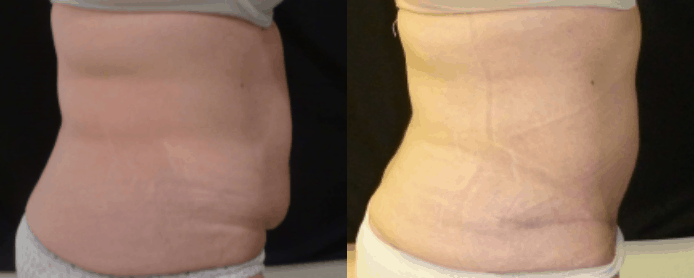
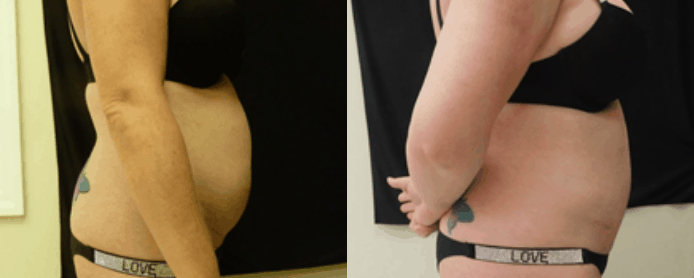
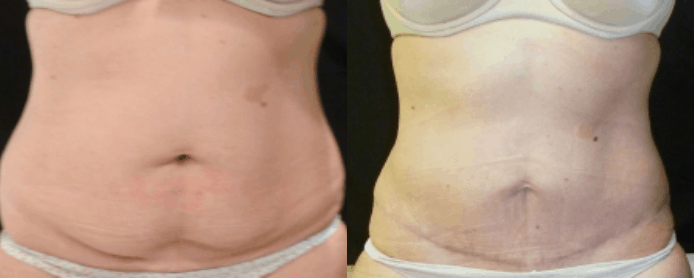
Reconstructive Surgeries
Hand Surgeries in Barrie, Ontario
Hand Surgeries
BPS offers various hand surgeries to help fix various hand injuries, conditions and diseases.
In Canada, most of the hand surgery and medical management of hand health problems is performed by plastic surgeons. Hand health problems include most of the problems for which people go to Emergency Departments. This includes infection, animal bites, burns, wounds of any kind, broken bones or any other problems seen daily in any Emergency Department. The more simple hand problems are managed by the Emergency room physicians. The more complex hand problems are generally referred to as plastic surgeons. Most broken bones of the hand heal with casting for a period of 2-4 weeks. However, some fractures will require surgery to better align the broken fragments. This is especially true if the break occurs into a joint where arthritis is more likely to occur if the broken fragments are not properly lined up.
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Stenosing Tenosynovitis
Benefits of Hand Surgery
De Quervain’s Tendonitis Syndrome
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Carpal Tunnel
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts are very common lumps within the hand and wrist that occur adjacent to joints or tendons. The most common locations are:
- the top of the wrist,
- the palm side of the wrist,
- the base of the finger on the palm side, and
- the top of the end joint of the finger.
The ganglion cyst often resembles a water balloon on a stalk and is filled with clear fluid or gel. The cause of these cysts is unknown, although they may form in the presence of joint or tendon irritation or mechanical changes. They occur in patients of all ages. These cysts may change in size or even disappear entirely, and they may or may not be painful. These cysts are not cancerous and will not spread to other areas.
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Dupuytren’s Disease
- The presence of a lump in the palm does not mean that surgery is required or that the disease will progress.
- Correction of finger position is best accomplished with milder contractures and contractures that affect the finger’s base. Complete correction sometimes can not be attained, especially of the middle and end joints in the finger.
- Skin grafts are sometimes required to cover open areas in the fingers if the skin is deficient.
- The nerves that provide feeling to the fingertips are often intertwined with the cords.
- Splinting and hand therapy are often required after surgery to maximize and maintain finger position and function improvement.
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Hand Surgeries
BPS offers various hand surgeries to help fix various hand injuries, conditions and diseases.
In Canada, most of the hand surgery and medical management of hand health problems is performed by plastic surgeons. Hand health problems include most of the problems for which people go to Emergency Departments. This includes infection, animal bites, burns, wounds of any kind, broken bones or any other problems seen daily in any Emergency Department. The more simple hand problems are managed by the Emergency room physicians. The more complex hand problems are generally referred to as plastic surgeons. Most broken bones of the hand heal with casting for a period of 2-4 weeks. However, some fractures will require surgery to better align the broken fragments. This is especially true if the break occurs into a joint where arthritis is more likely to occur if the broken fragments are not properly lined up.
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Stenosing Tenosynovitis
Benefits of Hand Surgery
De Quervain’s Tendonitis Syndrome
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Carpal Tunnel
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts are very common lumps within the hand and wrist that occur adjacent to joints or tendons. The most common locations are:
- the top of the wrist,
- the palm side of the wrist,
- the base of the finger on the palm side, and
- the top of the end joint of the finger.
The ganglion cyst often resembles a water balloon on a stalk and is filled with clear fluid or gel. The cause of these cysts is unknown, although they may form in the presence of joint or tendon irritation or mechanical changes. They occur in patients of all ages. These cysts may change in size or even disappear entirely, and they may or may not be painful. These cysts are not cancerous and will not spread to other areas.
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Dupuytren’s Disease
- The presence of a lump in the palm does not mean that surgery is required or that the disease will progress.
- Correction of finger position is best accomplished with milder contractures and contractures that affect the finger’s base. Complete correction sometimes can not be attained, especially of the middle and end joints in the finger.
- Skin grafts are sometimes required to cover open areas in the fingers if the skin is deficient.
- The nerves that provide feeling to the fingertips are often intertwined with the cords.
- Splinting and hand therapy are often required after surgery to maximize and maintain finger position and function improvement.
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Hand Surgeries
BPS offers various hand surgeries to help fix various hand injuries, conditions and diseases.
In Canada, most of the hand surgery and medical management of hand health problems is performed by plastic surgeons. Hand health problems include most of the problems for which people go to Emergency Departments. This includes infection, animal bites, burns, wounds of any kind, broken bones or any other problems seen daily in any Emergency Department. The more simple hand problems are managed by the Emergency room physicians. The more complex hand problems are generally referred to as plastic surgeons. Most broken bones of the hand heal with casting for a period of 2-4 weeks. However, some fractures will require surgery to better align the broken fragments. This is especially true if the break occurs into a joint where arthritis is more likely to occur if the broken fragments are not properly lined up.
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Stenosing Tenosynovitis
Benefits of Hand Surgery
De Quervain’s Tendonitis Syndrome
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Carpal Tunnel
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts are very common lumps within the hand and wrist that occur adjacent to joints or tendons. The most common locations are:
- the top of the wrist,
- the palm side of the wrist,
- the base of the finger on the palm side, and
- the top of the end joint of the finger.
The ganglion cyst often resembles a water balloon on a stalk and is filled with clear fluid or gel. The cause of these cysts is unknown, although they may form in the presence of joint or tendon irritation or mechanical changes. They occur in patients of all ages. These cysts may change in size or even disappear entirely, and they may or may not be painful. These cysts are not cancerous and will not spread to other areas.
Benefits of Hand Surgery
Dupuytren’s Disease
- The presence of a lump in the palm does not mean that surgery is required or that the disease will progress.
- Correction of finger position is best accomplished with milder contractures and contractures that affect the finger’s base. Complete correction sometimes can not be attained, especially of the middle and end joints in the finger.
- Skin grafts are sometimes required to cover open areas in the fingers if the skin is deficient.
- The nerves that provide feeling to the fingertips are often intertwined with the cords.
- Splinting and hand therapy are often required after surgery to maximize and maintain finger position and function improvement.